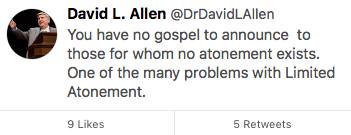
“What does synergism do? When consistently applied, it turns grace from the free action of God based upon His own purposes into a demanded provision for every human being. The result of this is that this provision, and in particular, the central act of that provision, the atoning sacrifice of the Lord Jesus, must become impersonal, theoretical, and unsaving, just so the autonomous will of man can be defended. Combine this with an unbiblical idea of evangelism (the idea that you proclaim what Jesus has done for you, thereby guilting people into doing something nice for Jesus in return, rather than the powerful command to every man, woman, and child to repent and believe in the Lord Jesus Christ), and you have the foundation for this tweet from one of the leading Southern Baptist “Traditionalists.” I am so thankful for the biblical reality, laid out so plainly in the book of Hebrews (ironically, a book upon which this synergistic writer has written a commentary!) that the death of my Lord was not a vague, impersonal, hypothetical action, but a powerful, purposeful act of redeeming grace, made in perfect harmony with the Father’s salvific decree and the Spirit’s salvific application, whereby the elect of God, united to the Son in His death, burial, and resurrection, receive perfect propitiation for their sins.”
– Dr. James White
The ground of the free offer of the gospel is not the extent of the atonement or election but that Christ is a perfect and sufficient savior and promises to save all those who repent and believe in Him.